Weekly U.S.-Mexico Border Update: Ciudad Ju?rez tragedy, Mexico …
With this series of weekly updates, WOLA seeks to cover the most important developments at the U.S.-Mexico border. See past weekly updates here.[1] Due to staff travel, we will publish next week's Border Update in an abbreviated format.
This week:
- The death toll now stands at 40 from a March 27 fire in a Ciudad Juarez migrant detention center.
Three low-ranking employees, a security guard, and a migrant have been indicted for homicide and intentional injury. The event has multiplied calls for accountability for abusive conditions in Mexico's migrant detention system.
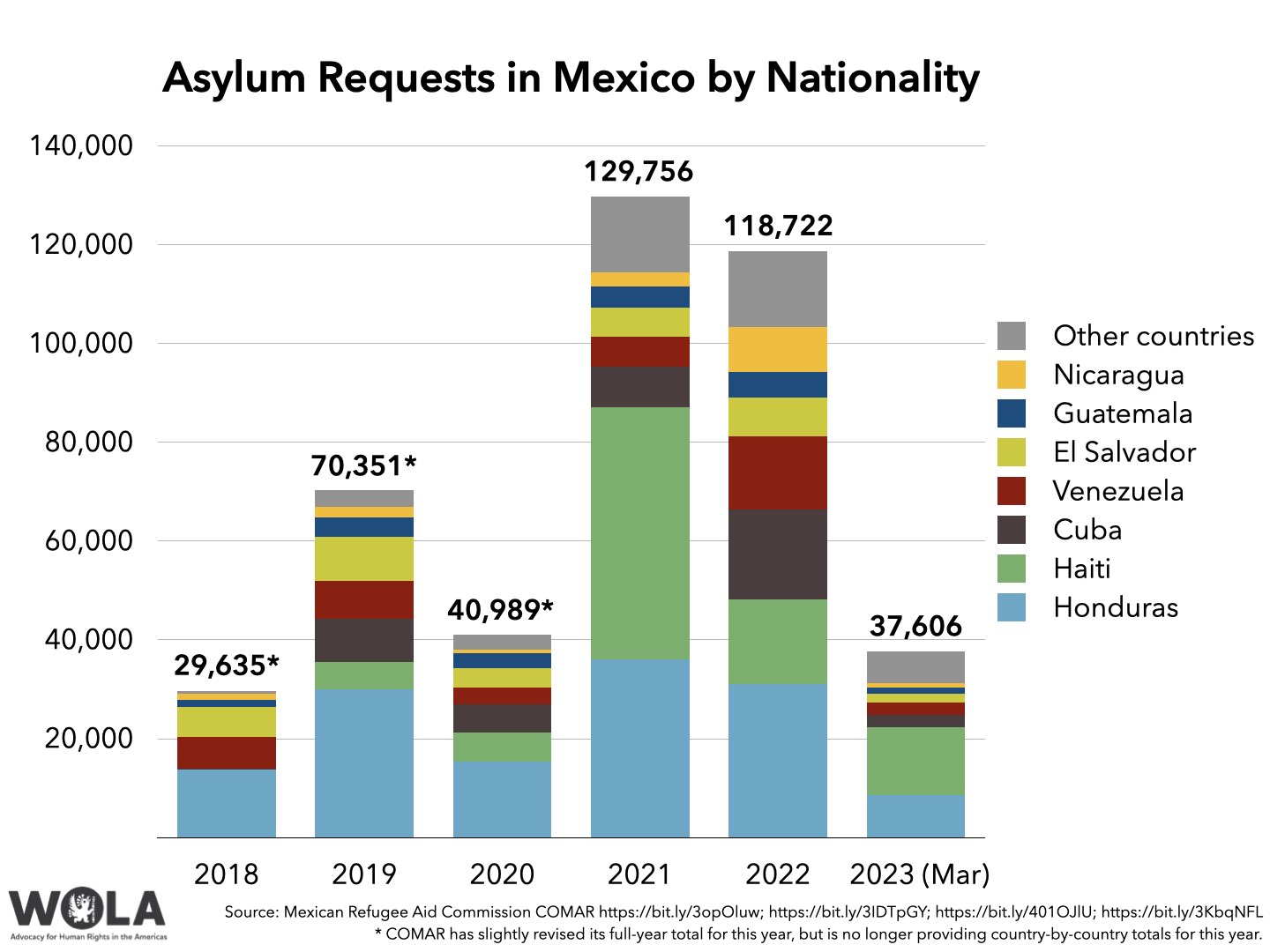
- Mexico's asylum system received more applications during the first quarter of 2023 than it has in the first quarter of any year. The most frequent nationality of applicants is Haiti.
In January and February, citizens most frequently apprehended by Mexican migration authorities were from Ecuador and Venezuela.
- About 1,200 people per day migrated through Panama's Darien Gap region in March. Of those making the hazardous 60-mile trip, 20 percent so far this year have been children. An average of five children per day have transited through the Darien Gap unaccompanied.
Fallout from Ciudad Juarez detention center fire
WOLA's March 31 Border Update reported[2] a death toll of "39 or more people" from a March 27 fire in a Mexican government provisional migrant detention center in Ciudad Juarez, just over the border from El Paso, Texas.
On April 3, Mexico's public security department increased[3] the count to 40 deaths: one of the men injured in the fire died[4] while being flown to a hospital in Mexico City. Not including this 40th individual, whose nationality was not reported, the fatal victims include[5] 18 Guatemalan migrants (most from the country's Indigenous-majority highlands), 7 Venezuelans, 6 Hondurans, 6 Salvadorans, 1 Colombian, and 1 Ecuadorian. As of March 30, 24 migrants were hospitalized[6] in serious or critical condition: 10 Guatemalans, 7 Hondurans, 4 Salvadorans, and 3 Venezuelans.
Mexico turned down a U.S. government offer to provide medical treatment to some of the injured in the United States, arguing that they were "too ill to be moved," the Associated Press reported[7]. Still, Mexico has since sought to fly some to specialized treatment in Mexico City. Troubling details about the tragedy continue to emerge. "Multiple testimonies" indicate that the facility had no emergency exits or fire extinguishers in its detention area, the daily Milenio reported[8].
Some of the detainees had been there for several days, or even since February, though the legal maximum is 36 hours. In the United States, relatives of the victims are complaining[9] that the Mexican government is not responding to inquiries or helping with the complicated repatriation of remains. Mexico's president, Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador, paid a visit[10] to Ciudad Juarez on March 31, where he said[11] that the tragedy "hurt me a lot, it damaged me." As the President's white van, with him in the passenger seat, drove through Ciudad Juarez's central square, it was detained for several minutes as mostly Venezuelan migrants surrounded the vehicle.
Lopez Obrador "opened the window and took the hand of a woman who pleaded with him as others pushed letters into his hand and cried for justicia, or justice, for the migrants," the El Paso Times reported[12]. One migrant reportedly[13] said to him, "Don't do what the United States does," to which he replied, "we are not the same, my love, don't confuse us." A Mexican federal judge ordered[14] the indictment, for homicide and intentional injury, of five people accused of involvement in the tragedy: three employees of Mexico's National Migration Institute (INM), one private security guard, and a Venezuelan migrant, Jeison Daniel Catari Rivas, accused[15] of setting fire to mattresses in protest, after guards allegedly said that the men in custody would be deported. "None of the public servants, nor the private security guards, took any action to open the door for the migrants who were inside where the fire was," said a federal human rights prosecutor cited[16] by the New York Times.
The INM has come under fire for the tragedy, especially after security camera footage showed personnel leaving the facility without opening the doors of a detention area filling with flames and smoke. While no source appears to have a current count, Pie de Pagina reported[17] that in 2019, INM was managing 30 detention centers throughout Mexico, plus an unknown number of provisional facilities like the one in Ciudad Juarez. "The majority of these centers," the online journalism outlet continued, citing a network of human rights groups, "lack potable water in bathrooms or toilets, and are places subject to inclement weather where the food that is delivered, in addition to being scarce, is often rotten. ...Private security personnel use threatening and abusive language with detainees, do not guarantee them the right to communicate with the outside world."
The Mexican government's public security secretary, Rosa Icela Rodriguez, said[18] that the Ciudad Juarez provisional detention center will not reopen. Upon apprehension in the city, migrants will be taken to the Mexican federal government's 900-capacity shelter, opened in 2019, where they are not confined. Rodriguez added[19] that Mexico's federal government has canceled its contract with Grupo de Seguridad Privada CAMSA, a company that was providing security guards to INM detention centers in 23 of Mexico's 32 states.
She noted that INM had "ignored the presidential order to hire elements of the Federal Protection Service (SPF) instead of private security companies, arguing that they are cheap," Milenio reported[20]. Other governments called for accountability for the tragedy. "El Salvador demands justice for this crime, which it considers a crime of the state," Border Report cited[21] Cindy Mariella Portal Salazar, El Salvador's vice minister for migrant affairs, as stating, adding that "she is not satisfied with the arrest of five guards and INM officers." A statement on Twitter from Honduras's Foreign Ministry called[22] for a "broad investigation" of Mexican authorities' responsibility. The Central American web outlet ContraCorriente noted[23] that three of Honduras's six victims were young men from the same town in western Honduras: El Nuevo Porvenir, which was completely destroyed by Hurricane Mitch in 1998.
U.S. human rights groups and some[24] reporting[25] continued to note[26] that the migrants' presence in Ciudad Juarez was a result of U.S. migration policy, which has made it very difficult for people to request asylum at the U.S.-Mexico border. All but two of the fire's victims were from countries whose citizens are subject to immediate expulsion back into Mexico, without a chance to ask for asylum, under the Title 42 pandemic order. The one means of making an appointment to ask for asylum from northern Mexico, the "CBP One" smartphone app, continues to be plagued by technical problems and a small number of available appointments.
The CBS News program 60 Minutes featured[27] the situation at the U.S.-Mexico border, documenting asylum seekers' difficulties with CBP One and interviewing DHS Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas. CBP One issues were also the subject of an episode[28] of Slate's What's Next TBD podcast. Those who fail to navigate the app remain stranded in Ciudad Juarez and other Mexican border cities.
Trends in migration through Mexico
Mexico's Refugee Aid Commission (Comision Mexicana de Ayuda a Refugiados, COMAR), which operates the country's asylum system, reported[29] receiving 37,606 applications for asylum in Mexico during the first three months of the year.
This is the largest number of asylum requests that Mexico has ever recorded during the first quarter of a year; if sustained over all of 2023 it would total over 150,000, a record by far. Applications jumped from 6,497 in January, to 6,932 in February, to 8,993 in March. So far this year, applications from citizens of Haiti are the most frequent with 13,631 (In addition, COMAR lists 1,344 from Brazil and 1,302 from Chile, noting[30] that most are children of Haitian citizens who had been residing in those countries).
Honduras (8,620), Cuba (2,596) and Venezuela (2,547) follow. Of 7,369 requests that COMAR has managed to process so far this year, it has granted asylum in 69 percent of cases (5,104).
During the final days of March, Mexico's Migration Policy Unit (Unidad de Politica Migratoria) published data[31] about authorities' apprehensions of migrants in Mexico through February 2023. The number-one nationality of migrants apprehended in Mexico in February was Venezuela 6,331, barely edging out Ecuador (6,249), which is actually the number-one nationality for the 2023 calendar year so far.
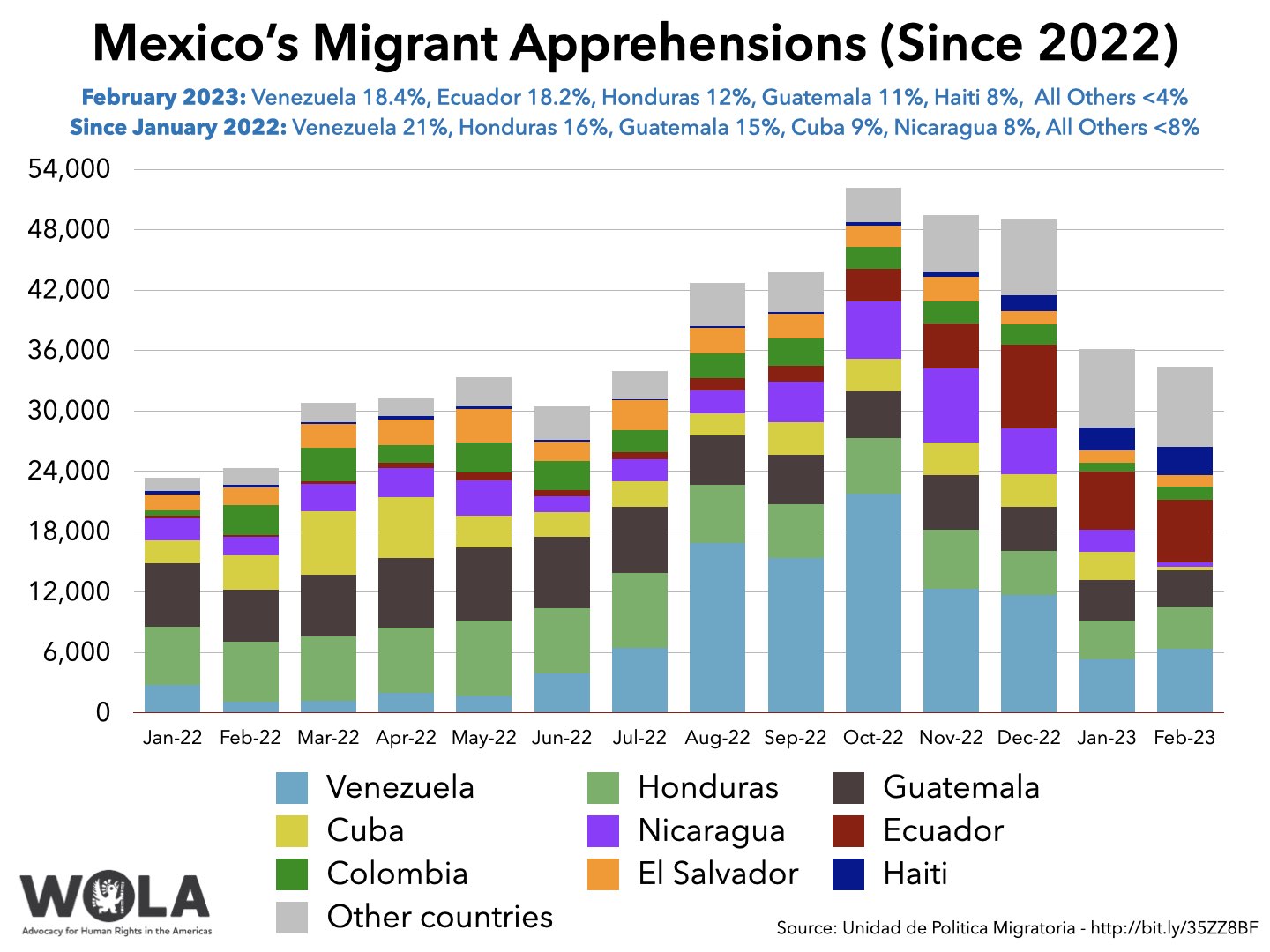
Mexico's apprehensions of Venezuelan migrants increased by over 1,000 over January, even though since October 2022, Venezuelans apprehended on the U.S. side of the border rarely get a chance to seek asylum: they are subject to Title 42 expulsion to Mexico. (In February, U.S. authorities encountered a majority of Venezuelan migrants at ports of entry, presumably with "CBP One" appointments.)
During the first two months of the year, Mexico has apprehended migrants from 101 countries. Enrique Lucero, the director of migration policy in the Tijuana mayor's office, told[32] Border Report that the city has seen an "ongoing flow" of migrants from Africa, mainly the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana and Somalia, who "are all taking the same route through Brazil, they'll cross South America and then on to Mexico City and finally Tijuana." Mexican border cities, like Tijuana and Ciudad Juarez, continue to host ever larger numbers of stranded migrants.
Shelters are now so full in Ciudad Juarez, Border Report found[33], that Central and South American migrants--including entire families--are now living in abandoned buildings and on the streets. Desperation is so great that the slightest rumor--like a Facebook message[34] on March 31--can cause large groups to cross the border at once. That day, more than 1,000 migrants, mostly from Venezuela, crossed[35] the Rio Grande and sought to turn themselves in to Border Patrol on the mistaken belief that they would be allowed to enter.
Notes from the Darien Gap
Further south, Panama has yet to publish March data[36] about migration through the treacherous Darien Gap jungle region.
Preliminary reports[37] indicate, though, that about 1,200 people per day migrated through the Darien region last month, which would put March 2023 on pace to be the third-heaviest month ever for Darien Gap migration. The 9,683 minors who traveled through the Darien Gap in January and February were "the most recorded in a two-month period since these records have been kept," according[38] to UNICEF. The agency estimated that an average of five children per day are making the 60-mile journey unaccompanied.
The chairman of the U.S. Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Government Affairs, Sen. Gary Peters (D-Michigan), visited[39] Panama, including the Darien Gap region, on April 4.
Migration through the Darien Gap was the subject of an April 5 panel[40] ( video[41]) at Columbia University featuring Nadja Drost and Federico Rios, two journalists who have transited this route alongside migrants.
Other news
- Preliminary March statistics that the conservative website The Center Square obtained[42] from an anonymous "U.S. Customs and Border Patrol [sic] agent" point to 169,842 "apprehensions" of migrants border-wide in March. If this number just counts Border Patrol apprehensions--excluding migrants who reported to ports of entry--it would be a 32 percent jump from the 128,877 migrants apprehended in February.
For the second straight month, the data point to Border Patrol's Tucson, Arizona Sector being the second-busiest of the agency's nine U.S.-Mexico border sectors, after El Paso.
- Witness at the Border's latest monthly report[43] monitoring U.S. deportation flights found that ICE carried out 145 removal flights in March, the "2nd highest month in over 3 years." 122 of those flights (84 percent) went to 4 destinations: Guatemala City (40 flights in March), Ecuador (number 2 for the third straight month with 31 flights), Honduras (27), and Colombia (24).
- The Los Angeles Times examined[44] conditions in seven countries from which large numbers of people have been migrating.
- Border Patrol's Tucson, Arizona Sector leads all nine of the agency's U.S.-Mexico border sectors in use of force incidents, the Arizona Daily Star reported[45].
- During the present congressional recess, Sen. Kyrsten Sinema (I-Arizona) is leading[46] a delegation of generally moderate Republican legislators to rural Arizona segments of the border. It includes Sen.
Thom Tillis (R-North Carolina), Rep. Juan Ciscomani (R-Arizona), Rep. Tony Gonzales (R-Texas), and Rep.
David Valadao (R-California).
- The U.S.
Forest Service reopened a segment of border-area territory where Arizona's last governor, Doug Ducey (R), had installed miles of empty shipping containers to fill gaps in the border wall. "The construction, then removal, of shipping container walls in Yuma and at the Coronado National Forest in Cochise County, cost Arizona taxpayers more than £200 million," reported[47] the Border Chronicle.
- Mexico's consul-general in San Diego said[48] that a three-month-old Mexican police program to screen vehicles approaching the United States at the busy San Ysidro port of entry "has cut down on illegal driving attempts into the U.S. from about 10 daily to only four."
- A commentary[49] from the Project on Government Oversight warned of the Biden administration's plans to place asylum seekers in expedited removal proceedings, in which they must defend their cases while in austere CBP custody within a few days of apprehension. "If asylum seekers are deported back to danger before ever having the chance to speak to lawyers or have private phone calls, if their only interviews with asylum officers take place in Border Patrol jails where guards might overhear, there will be even less recourse."
References
- ^ here (www.wola.org)
- ^ reported (www.wola.org)
- ^ increased (www.gob.mx)
- ^ died (apnews.com)
- ^ include (es-us.noticias.yahoo.com)
- ^ hospitalized (www.milenio.com)
- ^ reported (apnews.com)
- ^ reported (www.milenio.com)
- ^ complaining (www.prensalibre.com)
- ^ visit (laverdadjuarez.com)
- ^ said (laverdadjuarez.com)
- ^ reported (www.elpasotimes.com)
- ^ reportedly (www.milenio.com)
- ^ ordered (www.milenio.com)
- ^ accused (laverdadjuarez.com)
- ^ cited (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ reported (piedepagina.mx)
- ^ said (www.milenio.com)
- ^ added (apnews.com)
- ^ reported (www.milenio.com)
- ^ cited (www.borderreport.com)
- ^ called (efectococuyo.com)
- ^ noted (contracorriente.red)
- ^ some (time.com)
- ^ reporting (www.axios.com)
- ^ note (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ featured (www.cbsnews.com)
- ^ episode (slate.com)
- ^ reported (www.gob.mx)
- ^ noting (twitter.com)
- ^ published data (politicamigratoria.gob.mx)
- ^ told (www.borderreport.com)
- ^ found (www.borderreport.com)
- ^ message (www.nbcnews.com)
- ^ crossed (www.cbp.gov)
- ^ data (www.migracion.gob.pa)
- ^ reports (www.minseg.gob.pa)
- ^ according (efectococuyo.com)
- ^ visited (twitter.com)
- ^ panel (ilas.columbia.edu)
- ^ video (www.youtube.com)
- ^ obtained (www.thecentersquare.com)
- ^ monthly report (witnessattheborder.org)
- ^ examined (www.latimes.com)
- ^ reported (tucson.com)
- ^ leading (www.sinema.senate.gov)
- ^ reported (www.theborderchronicle.com)
- ^ said (www.borderreport.com)
- ^ commentary (www.pogo.org)